Internationalization of Indian Rupee – RBI’s major move to settle worldwide transactions in Indian Rupee

India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) – the impact of bilateral ties and international trade
March 25, 2022
The prospects of the emerging trade ties between India and Australia
July 13, 2022To promote growth of global trade with emphasis on exports from India and to support the increasing interest of global trading community in INR, Reserve bank of India (RBI) puts in place an additional arrangement for invoicing, payment, and settlement of exports/imports in INR. This means that now the exports and imports will be denominated in rupees. It is expected that this move will reduce the demand for dollars and lead to a reduction in foreign currency risks and exchange rate risks due to forex fluctuations.

It can lower transaction costs of cross-border trade and investment operations by mitigating exchange rate risk but makes the simultaneous pursuit of exchange rate stability and a domestically oriented monetary policy more challenging, unless supported by large and deep domestic financial markets that could effectively absorb external shocks.
The broad framework for cross border trade transactions in INR under Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA) is as delineated below:
- Invoicing: All exports and imports under this arrangement may be denominated and invoiced in Rupee (INR).
- Exchange Rate: Exchange rate between the currencies of the two trading partner countries may be market determined.
- Settlement: The settlement of trade transactions under this arrangement shall take place in INR in accordance with the procedure laid down in Para 3 of this circular.

Further, in terms of Regulation 7(1) of Foreign Exchange Management (Deposit) Regulations, 2016, AD[1] banks in India have been permitted to open Rupee Vostro Accounts. Accordingly, for settlement of trade transactions with any country, AD bank in India may open Special Rupee Vostro Accounts of correspondent bank/s of the partner trading country. To allow settlement of international trade transactions through this arrangement, it has been decided that:
- Indian importers undertaking imports through this mechanism shall make payment in INR which shall be credited into the Special Vostro account of the correspondent bank of the partner country, against the invoices for the supply of goods or services from the overseas seller /supplier.
- Indian exporters, undertaking exports of goods and services through this mechanism, shall be paid the export proceeds in INR from the balances in the designated Special Vostro account of the correspondent bank of the partner country.
At times of inflationary pressures, higher than the world average inflation rate undermines the use of the currency as an international medium of exchange and a store of value and can restrict the role of such an economy in global value chains. Thus, the primary focus of flexible inflation targeting framework on price stability augurs well for further liberalisation of the capital account and internationalisation of the rupee.
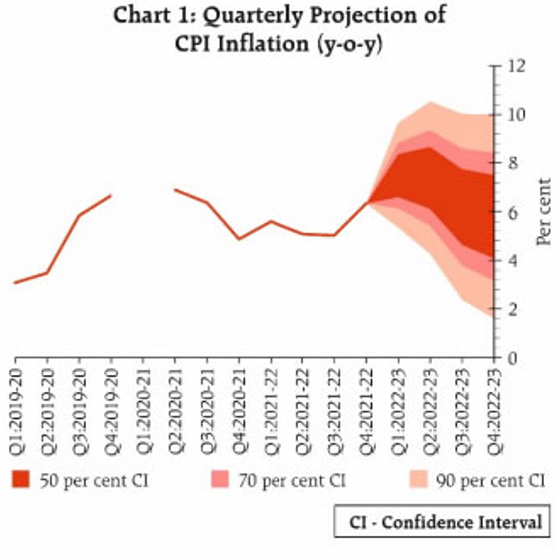
With countries facing foreign exchange shortages, use of rupees as a medium of forex would largely reduce the risk and burden associated with dollar in recent times. Along with benefits to exports it would also lower the transaction costs involved in international trade. For instance, with Russia sanctions in place, trade has almost come to a halt due to payment problems. As a result of the trade-facilitation mechanism introduced by the RBI, we see payment issues with Russia easing.
In the process of phased adoption of the same, the RBI would have to be careful in managing the stability of money supply and interest rate especially with soaring inflation in Indian economy despite the RBI’s inflation targeting policies. RBI monitors the exchange rates as a key information variable for monetary policy formulation as inflation can still alter by 10-13 per cent of the change in exchange rate. A stable and efficient domestic financial market will also help absorb the external shocks with exchange rate now being determined by market completely and capital account progressively being fully convertible.
#Intueri’s Views
Antara Mukherjee
[1] Authorised Dealer Banks




