Industry 4.0 consulting: Digitizing the Life Science sector

International Trade and Global Value Chain-Hypothesis and Implications
May 13, 2019
Monetary Policy and Inflation Dynamics in Major ASEAN Economies
June 12, 2019The invention of the steam engine set the stage for the first industrial revolution that took place in the 18th century, mechanizing a lot of works in the agrarian sector. The next revolution was fueled by electricity and paved the way for mass production. The third industrial era witnessed the rise of automation, powered by computers and robotics. And now we have entered the next phase of evolution in the manufacturing space — the Industry 4.0 era. The fourth industrial revolution has often been defined as the information-intensive evolution of manufacturing facilities where humans and machines interact via the Internet of Things (IoT) to optimize the operations and productivity. Life Science is one of the sectors that can gain an immense competitive edge by embracing a new, innovative business model, powered by advanced technologies. Reports have suggested that the adoption of disruptive technologies can transform the manufacturing value chain in the Life Science industry. In fact, some big ticket companies in this sector have already started turning the innovations into new opportunities.
The Reimagining of the Life Science Sector in the Age of Industry 4.0

A few years back, in one of its blogs, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) pointed out why the pharmaceutical manufacturers should be encouraged to transition from batch manufacturing to continuous manufacturing. The pharmaceutical industry is becoming overly competitive with more generic drugs entering the market. In this situation, such a transition, according to FDA, would not only ensure the quality of drugs but also reduce the high costs relating to batch manufacturing. No wonder, some major life science and pharmaceutical brands have adopted the Industry 4.0 to reap the benefits of the new-age technologies. Here are a few ways, these firms are reaping the Industry 4.0 benefits.
Ease of Supply Chain Management: First of all, with the increasing interaction between the physical and virtual, it will be possible to set up next-gen supply chains that are analytics-driven and can be monitored and controlled through a centralized system in real time. For example, in the developing countries that have a complex distribution and warehousing system, Pharma companies are using cloud-based supply chain management solutions for the better management of inventory and support recalls.
A Widened Scope of Innovation: Clinical research involves dealing with an enormous amount of data. Massive and costly infrastructure is needed to mine, analyze and simulate the data. This costly process can be avoided by integrating cloud-based solutions across a company’s research facilities, irrespective of their geographical locations. These data can then be accessed by disparate teams stationed in different locations for analysis. This system is helping minimize the time and expenses relating to trials. This wider access to data and information is, in turn, making open innovations possible.
Modernization of the Operations Through Automation: Companies are bypassing manual steps with automation. An increasing number of medical device manufacturing facilities are integrating Process Analytical Technologies (PAT) system into assembly lines to speed up production while optimizing the batch quality and minimizing wastes and production costs.
The Life Sciences sector is currently under tremendous pressure resulting from several factors, namely an ever-ageing world population, a faster spread of diseases due to increasing international travel, and the phenomenal rise in the chronic diseases. The companies are struggling to meet huge consumer expectations of coming up with new, cutting-edge drugs that save more lives. In this situation, moving forward, it will become increasingly difficult for companies to stay in business unless they opt for an Industry 4.0 makeover.
The Path to Industry 4.0 Adoption
As with any major shift, companies should be prepared for facing challenges while adopting an Industry 4.0 model. Any technological misstep may translate into costly production outage. Even then, there are several reasons why growth-oriented pharma companies should consider taking the plunge albeit its challenges. They should explore ways to reap the benefits of Big Data solutions, integrate IoT and wearable technologies for a more accurate diagnostic and patient outcomes, and adopt a higher level of across-the-channel collaboration for a better patient experience to name a few. The question, then, is not if a company should become Industry 4.0 ready, but how to go about it. All, one needs is the right strategy and Industry 4.0 consultations.
Intueri’s Industry 4.0 Implementation Approach
We, at Intueri, believe that Industry 4.0 is not a finite system or think – it is a natural evolution using technology to add intelligence to all existing assets manufacturing/supply system. The main intention of the exercise is to drive efficiency, flexibility, quality and lower operating expenses throughout production. We think many companies tend to focus on technology first, forgetting to anchor it in the real issues and linking it to the actual problems on the shop floor. This strategy of “going full gadgets” is tempting, but it rarely creates any real impact.
Intueri’s approach to Industry 4.0 aims to tackle this challenge and is quite simple: start small with a proof of concept of Industry 4.0, realizing its benefits, and then scale-up to conduct organization-wide Industry 4.0 implementation.
To provide guidance and support to align business strategies and operations with Industry 4.0, Intueri uses an Industry 4.0 maturity model to systematically assess a company’s state-of-development in relation to the Industry 4.0 vision. The practical purpose of this work aims at rigorously evaluating a company’s Industry 4.0 maturity and reflect the fitness of current strategies.
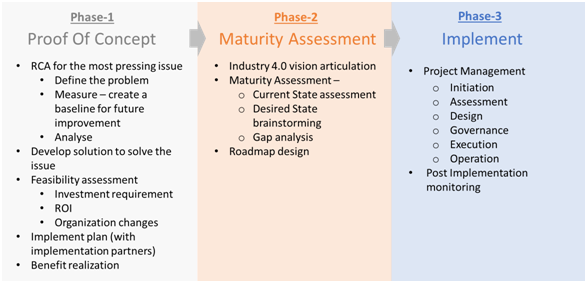
Intueri manages the whole Industry 4.0 implementation into three phases. The first phase involves a Proof of Concept of Industry 4.0, by tackling the organization’s most pressing issue. In the second phase, Intueri conducts a comprehensive Industry 4.0 maturity and feasibility assessment for the organization, and roadmap design for Industry 4.0 implementation. The third phase will involve implementation and post-implementation monitoring.